Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common type of sleep disorder in adults, characterized by the upper airway collapsing during sleep, causing pauses in breathing. People with obstructive sleep apnea often snore loudly and experience excessive daytime sleepiness. The risk of obstructive sleep apnea increases with factors such as obesity, family history of sleep apnea, and tonsil size. The diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea is typically done through a sleep laboratory study or an at-home sleep apnea test. Common symptoms of sleep apnea include waking up gasping for air, morning headaches, and dry mouth. Treatment options for obstructive sleep apnea include the use of a positive airway pressure device or surgery to un obstruct the airway.
What is sleep apnea and its types?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep-related breathing disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. One of the most common types of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea in adults, where the throat muscles relax and block the airway. This can lead to pauses in breathing and affect the quality of sleep. People with sleep apnea might experience daytime symptoms such as feeling tired or falling asleep at work. Additionally, sleep apnea can increase the risk of cardiovascular and other medical conditions, such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. It is important to recognize the signs of sleep apnea and seek treatment from a sleep medicine specialist if diagnosed.
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the throat muscles in the back of the throat relax and block the airway during sleep. People with obstructive sleep apnea are more likely to have obstructive sleep apnea, which can affect their sleep habits and restorative sleep. Treatment for obstructive sleep apnea may include CPAP therapy or other treatments for obstructive sleep apnea to help keep the airway open during sleep.
Central sleep apnea is another type of sleep apnea that is associated with pauses in breathing during sleep. People with central sleep apnea often have severe symptoms and may need to stay at a specialized sleep center for monitoring and treatment. The risk of central sleep apnea is not as common as obstructive sleep apnea, but it is still important to recognize the signs and seek treatment for sleep apnea if diagnosed.
Understanding apnea and its impact on sleep quality
Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder that can lead to feelings of exhaustion and grogginess during the day. It is a collection of sleep conditions that can affect the quality of sleep. Understanding apnea and how it impacts sleep quality is essential for individuals who may be at risk for sleep apnea. One form of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea, which occurs when the muscles in the throat relax, causing a narrow airway. Another type, central sleep apnea, is typically diagnosed in a specialized sleep lab.
Differentiating obstructive sleep apnea from central sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is a common sleep problem that leaves people living with sleep apnea repeatedly stopping and starting their breathing during sleep. On the other hand, central sleep apnea is a group of sleep disorders associated with sleep apnea, where the brain fails to send signals to the muscles that control breathing. A doctor will typically diagnose obstructive sleep apnea after a thorough examination, which may include a sleep study at a specialized sleep laboratory. Men are 2 to 3 times more likely than women to have obstructive sleep apnea risk factors. If a Mayo Clinic patient experiences symptoms like loud snoring, morning headaches, or fatigue during the day, they should consult a healthcare provider to determine if they have sleep apnea. Differentiating between the two types of sleep apnea is crucial in developing a proper treatment plan to help individuals reduce their symptoms and improve their sleep quality. Sleep apnea can occur in both obstructive and central forms, but understanding the differences in a person’s symptoms is essential for effective management.
People with sleep apnea may relax during sleep to where their airway becomes blocked, leading to obstructive sleep apnea. In contrast, individuals with central sleep apnea may fail to breathe properly because their brain fails to send the necessary signals to the muscles. It is important to note that both obstructive and central sleep apnea can disrupt a person’s sleep and overall health. If symptoms sound familiar, it is vital to seek a healthcare professional’s advice to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan to address the sleep problem effectively. Better sleep starts with understanding the differences between the two types of sleep apnea and taking proactive steps to manage the condition.
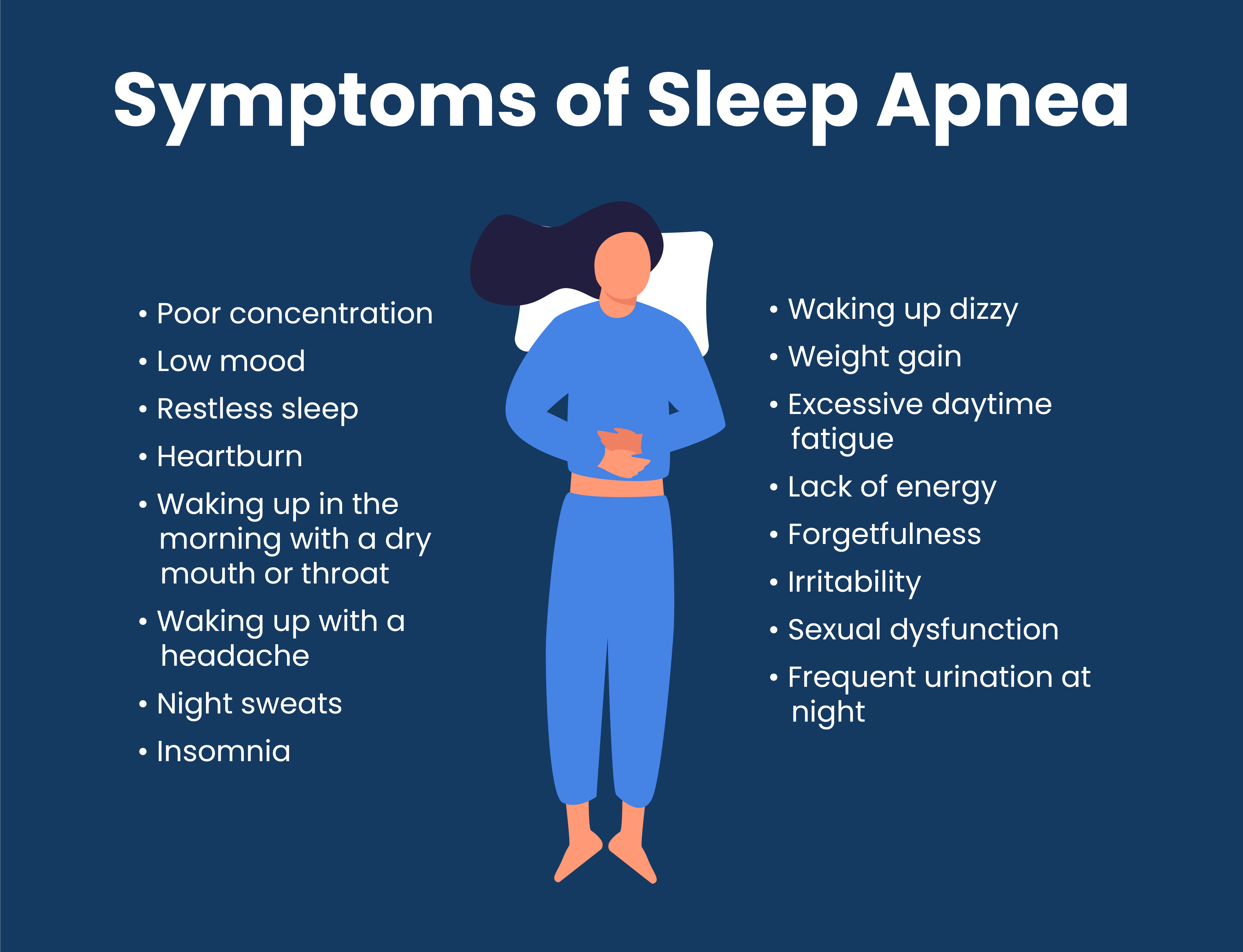
Identifying Symptoms and Causes
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder where breathing stops and starts repeatedly during sleep. One of the most common symptoms of sleep apnea is loud snoring, which can be disruptive to both the person suffering from it and their sleeping partner. Another common symptom is feeling excessively tired throughout the day, despite getting what seems like a full night’s sleep. If you suspect you may have sleep apnea, it is important to see a doctor to get properly diagnosed.
There are several causes of sleep apnea, including a blockage in the airway that causes breathing to stop momentarily. The tongue may forward during sleep, or the throat muscles may relax excessively, causing this blockage. In some cases, certain medicines and general anesthesia can also contribute to the development of sleep apnea.
Potential causes and risk factors contributing to sleep apnea development
There are several potential causes and risk factors that can contribute to the development of symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea. One common cause is obesity, as excess weight can lead to increased pressure on the airways during sleep. Additionally, having a large neck circumference or a narrow airway can also increase the risk of developing symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea. Genetics may also play a role, as individuals with a family history of sleep apnea are more likely to develop the condition themselves. In addition, certain lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and sedative use can also increase the risk of sleep apnea, which is typically diagnosed.
Overall, it is important to be aware of these potential causes and risk factors in order to take steps to prevent or manage obstructive sleep apnea. Seeking treatment from a healthcare professional is essential in order to properly diagnose and manage the condition. By addressing these risk factors and making necessary lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing and experiencing the symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea.
How obstructive sleep apnea affects oxygen levels during sleep
Obstructive sleep apnea is a condition where the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing and a decrease in oxygen levels. This disorder can have serious consequences for a person’s health, as interrupted breathing can lead to low oxygen levels in the blood, a condition known as hypoxemia. During episodes of obstructive sleep apnea, the body is deprived of oxygen, causing the brain to signal the body to wake up and resume breathing. This disrupted sleep pattern can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, and other symptoms. Over time, untreated obstructive sleep apnea can increase the risk of cardiovascular issues, hypertension, and other health problems. Monitoring oxygen levels during sleep can help diagnose and manage obstructive sleep apnea effectively.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
When it comes to diagnosis, healthcare providers rely on a variety of tools and tests to pinpoint the root cause of a patient’s symptoms. These may include physical examinations, blood tests, imaging scans, and biopsies. Once a diagnosis has been made, the next step is to discuss treatment options with the patient.
There are several treatment options available, depending on the specific condition being treated. These may include medication, laser treatment, oral appliances, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes. The best course of action will depend on the individual patient’s needs and preferences, as well as the severity of the condition.
In some cases, a combination of treatments may be recommended to achieve the best results. It’s important for patients to have open and honest discussions with their healthcare providers to ensure they are receiving the most appropriate care for their condition.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Prevention and management strategies are key to dealing with obstructive conditions, such as asthma and sleep apnea. Early intervention is crucial in order to accurately diagnose and treat these conditions before they worsen. One important prevention strategy is to avoid triggers that can exacerbate symptoms, such as tobacco smoke or allergens. It’s crucial for people who have already received a diagnosis of an obstructive condition to adhere to a healthcare provider’s recommended treatment plan, which may include medication, lifestyle changes, and routine monitoring. Additionally, implementing strategies to improve overall respiratory health, such as regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight, can help manage symptoms and prevent disease progression.
Understanding the family history and implications of sleep apnea
It is important to consider family history when evaluating the risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea. This condition can run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition to the disorder. By understanding the family history of sleep apnea, healthcare providers can better anticipate and diagnose the condition in relatives. Individuals with a family history of sleep apnea should remain vigilant for symptoms such as loud snoring, daytime fatigue, and pauses in breathing during sleep. Seeking a proper diagnosis and treatment is crucial in order to improve quality of life and reduce the risk of complications associated with untreated sleep apnea.
Exploring ways to reduce the risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can have serious health consequences if left untreated. Fortunately, there are several ways to reduce the risk of developing this condition. One of the most important steps is to maintain a healthy weight, as obesity is a major risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea. Additionally, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime can help prevent the relaxation of throat muscles, which can lead to obstructive sleep apnea. It is also important to practice good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine. If you suspect that you may have obstructive sleep apnea, it is crucial to seek medical help and undergo a sleep study to accurately diagnose the condition and receive appropriate treatment. By taking these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea and improve your overall health and quality of life.
Importance of consulting a dentist or sleep specialist for sleep apnea concerns
Consulting a dentist or sleep specialist for concerns related to sleep apnea is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Sleep apnea is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on overall health and quality of life. Only a trained medical professional can diagnose obstructive sleep apnea through various tests and assessments. By seeking help from a specialist, individuals can receive personalized treatment plans tailored to their specific needs. Additionally, a doctor can also help monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to ensure optimal results. Ignoring the symptoms of sleep apnea can lead to serious health complications, so it is important to seek medical advice as soon as possible.