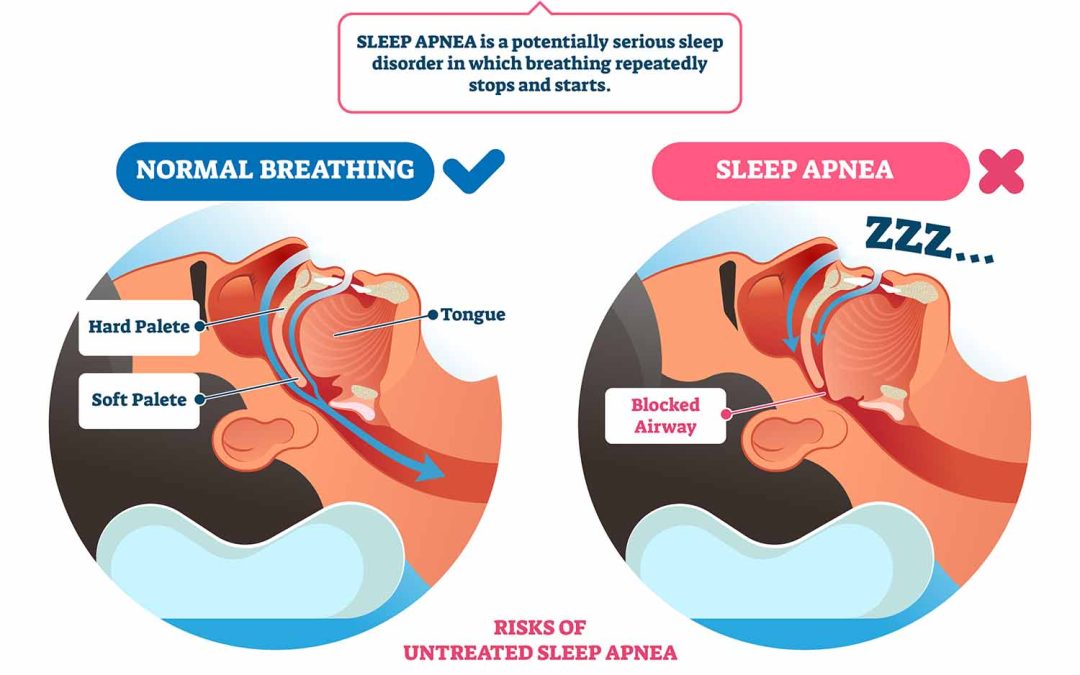
What is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that causes interruptions in breathing during sleep. There are two main types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). When the soft tissue at the back of the throat blocks the airway, obstructive sleep apnea results. This can cause a person to snore loudly and have low oxygen levels during sleep. On the other hand, central sleep apnea is a disorder where the brain fails to signal the muscles to breathe because of instability in the respiratory control center. This form of sleep apnea is more rare but can be just as serious. Both types of sleep apnea can reduce sleep quality and increase the risk of other health conditions.
Symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea in adults include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, and daytime fatigue. People with central sleep apnea may experience treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, which is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea. If left untreated, sleep apnea can cause severe sleep apnea, putting individuals at a higher risk of developing other health issues such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. It is important for individuals who suspect they have sleep apnea to seek help from a doctor or sleep specialist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Types of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea usually falls into two categories: obstructive or central sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea happens when your throat muscles relax and block your airway, leading to breathing problems during sleep. Central sleep apnea often occurs in people with certain medical conditions that affect the brainstem. Children with obstructive sleep apnea may have enlarged tonsils and adenoids, which can be a common cause of the condition. If your sleep apnea increases your risk for central sleep apnea, your doctor may refer you to a sleep medicine specialist for further evaluation. The severity of sleep apnea can vary from mild sleep apnea to more severe cases that require treatment.
Treatment for sleep apnea depends on the underlying cause. For obstructive sleep apnea, surgery to remove the tonsils and adenoids may be recommended. Central sleep apnea is usually treated with medications or devices to help you breathe more effectively during sleep. People assigned male at birth are more likely to have obstructive sleep apnea, but anyone can develop the condition. Sleep apnea increases your risk of other health problems, such as high blood pressure and heart disease. If you suspect you have sleep apnea, it’s important to talk to your doctor about symptoms and causes.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that involves disrupted breathing during sleep. The cause of obstructive sleep apnea is a blockage of the airway during sleep, frequently because of the throat muscles relaxing. The symptoms of sleep apnea may include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, and feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep. If left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to serious sleep and health issues. It is important to seek treatment for sleep apnea to ease your symptoms and improve your overall well-being.
Risk Factors for Sleep Apnea
Risk Factors for Sleep Apnea involve various factors that can increase the sleep apnea risk in individuals. A blockage of the airway during sleep is what causes obstructive sleep apnea, whereas complex sleep apnea also carries the risk of central sleep apnea. People with sleep apnea experience breathing interruptions repeatedly during sleep, leading to poor sleep quality and potential health risks. Treatment of sleep apnea may involve a visit to a sleep center for a night in a sleep clinic to diagnose and treat sleep issues. Depending on the type of sleep apnea diagnosed, the treatment may vary. For instance, the treatment for central sleep apnea may differ from that of obstructive sleep apnea, but it is equally important in helping individuals sleep through the night and cause symptoms associated with this serious sleep disorder.
Causes and Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can be attributed to a variety of factors, such as obesity, genetics, enlarged tonsils, and hormonal disorders. When a person sleeps, the muscles in the throat relax, causing the airway to become obstructed and resulting in pauses in breathing during sleep. This can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels in the blood and disrupt the normal sleep stages.
At Sleep Solutions, patients suspected of having sleep apnea may undergo a series of diagnostic tests to determine the severity of the condition. These tests can include using a portable at-home device to monitor breathing patterns while sleeping. Once diagnosed, there are various treatment options available to treat sleep apnea, such as oral appliance therapy and Nightlase laser snoring treatment.
Obstructive vs. Central Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the muscles in the throat relax during sleep, causing the airway to become blocked. This obstruction leads to pauses in breathing and can result in loud snoring or gasping for air. Individuals with obstructive sleep apnea often experience daytime fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating because of interrupted sleep patterns. Treatment options for obstructive sleep apnea may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss or avoiding alcohol before bedtime, as well as the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices.
Central sleep apnea, on the other hand, is a neurological disorder that occurs when the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles responsible for controlling breathing. Unlike obstructive sleep apnea, there is no physical obstruction in the airway. Symptoms of central sleep apnea may include shortness of breath, insomnia, and frequent awakenings during the night. Treatment options for central sleep apnea may involve addressing underlying medical conditions, such as heart failure or stroke, that may be contributing to the disorder.
Sleep Studies for Diagnosis
At Sleep Solutions, we use sleep studies as diagnostic tools to assess and identify sleep disorders. These studies can provide valuable information about a person’s sleep patterns, quality of sleep, and potential underlying medical conditions that may be affecting their ability to get a good night’s rest. By monitoring heart rate, breathing patterns, and movement during sleep, we can identify issues such as sleep apnea, insomnia, narcolepsy, and restless legs syndrome. Overall, sleep studies play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating a variety of sleep disorders, ultimately improving the overall health and well-being of patients.
Common Causes of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people around the world. There are several common causes of sleep apnea that can contribute to the condition. One of the main causes is obesity, as excess weight can put pressure on the airway and make it difficult to breathe properly during sleep. Another common cause is physical abnormalities in the airway, such as enlarged tonsils or a deviated septum, which can block the airway and lead to breathing problems. Smoking is also a common cause of sleep apnea, as it can irritate the airway and lead to inflammation that restricts airflow. Additionally, alcohol consumption before bed can relax the muscles in the throat and make it more likely for the airway to become blocked during sleep. Understanding these common causes can help individuals take steps to manage their sleep apnea and improve their quality of sleep.
Living with Sleep Apnea: Tips and Advice
Sleep apnea can make it difficult to get a good night’s rest, leading to feelings of exhaustion and irritability during the day. A blockage of the airway is what causes obstructive sleep apnea, which frequently causes breathing pauses while you sleep. To help manage the symptoms of sleep apnea, there are several tips and pieces of advice to consider.
One important tip is to maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can contribute to the obstruction of the airway. Additionally, sleeping on your side instead of your back can help keep the airway open during sleep. Avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime can help prevent the relaxation of the throat muscles, which can exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms. With these tips and advice, it is possible to improve the quality of sleep and overall well-being while living with sleep apnea.
Potential Health Complications of Untreated Sleep Apnea
Untreated sleep apnea can lead to a variety of health complications if left unchecked. Without intervention, individuals with signs of sleep apnea may experience chronic fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating because of disrupted sleep patterns. Additionally, a lack of quality sleep can have a detrimental effect on overall physical and mental well-being. In severe cases, untreated sleep apnea can increase the risk of cardiovascular issues such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. This is why it is essential to seek treatment to improve sleep quality and reduce the potential health risks associated with sleep apnea.
Let Sleep Solutions Guide You
At Sleep Solutions in Westborough, MA, we focus on treating sleep apnea and snoring through oral appliance therapy and Nightlase laser snoring therapy. Reserve some time with us today to get started on your path to better sleep and better health.